Understanding Shame and Self-Hatred
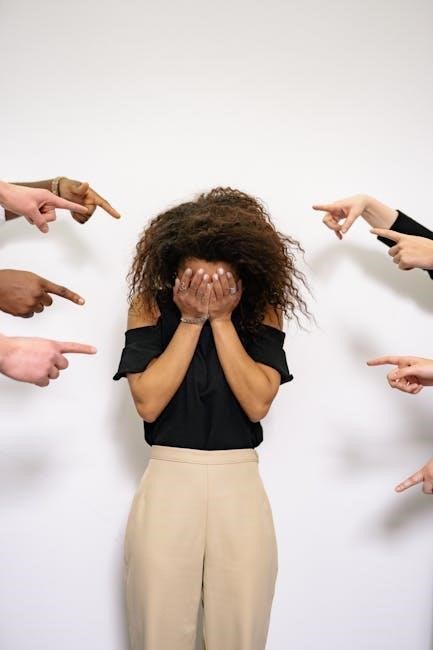
Shame and self-hatred are deeply rooted, emotional responses often stemming from trauma, societal expectations, or negative self-talk, significantly impacting mental health and self-perception.
Defining Shame and Self-Hatred
Shame is a deeply painful emotion involving self-criticism and a sense of worthlessness, often triggered by perceived failure or external judgment. It differs from guilt, which focuses on specific actions, as shame centers on the self. Self-hatred, a more intense and chronic form of self-criticism, involves persistent negative self-judgment and a lack of self-compassion. Both emotions can stem from childhood trauma, societal expectations, or internalized negativity. Understanding these definitions is crucial for addressing their impact on mental health and well-being. By recognizing shame and self-hatred as emotional responses rather than absolute truths, individuals can begin the process of healing and rebuilding a healthier self-image. These definitions provide a foundation for exploring their origins and developing strategies to overcome them.
The Difference Between Shame and Guilt
Shame and guilt, while often confused, are distinct emotions with different focuses. Guilt arises from regret over a specific action or behavior, often prompting remorse and a desire to make amends. In contrast, shame is a deeper, more pervasive emotion rooted in self-perception, involving feelings of worthlessness or inadequacy. Guilt is about what you did, while shame is about who you are. For example, guilt might lead someone to apologize for a mistake, while shame might cause them to believe they are inherently flawed. Understanding this distinction is vital, as guilt can motivate positive change, whereas shame often leads to self-punishment and hiding. Recognizing the difference is the first step toward addressing these emotions constructively and fostering personal growth. This clarity is essential for healing and rebuilding self-worth.
How Shame and Self-Hatred Manifest
Shame and self-hatred often manifest in subtle yet profound ways, deeply impacting emotional and psychological well-being. Emotionally, they may appear as persistent self-criticism, feelings of inadequacy, or a tendency to internalize blame. Behaviorally, individuals might engage in self-sabotaging behaviors, withdraw from social interactions, or struggle with setting healthy boundaries. Physically, shame can show up as slouched posture, avoiding eye contact, or other nonverbal cues of self-diminishment. Self-hatred often fuels negative self-talk, where individuals may harshly judge themselves, replay past mistakes, or believe they are unworthy of love or success. These patterns can become deeply ingrained, making it difficult to recognize and challenge them. Over time, unchecked shame and self-hatred can contribute to mental health issues like depression, anxiety, or low self-esteem, underscoring the importance of addressing these emotions proactively. Recognizing these manifestations is the first step toward healing.

Identifying the Roots of Shame and Self-Hatred
Shame and self-hatred often stem from childhood trauma, societal expectations, or internalized negative beliefs, requiring exploration to understand their origins and address their impact on self-perception.
Childhood Trauma and Its Impact
Childhood trauma, such as emotional neglect or abuse, profoundly shapes self-perception, often leading to deep-seated shame and self-hatred. Negative messages internalized during formative years can create a belief system where individuals view themselves as unworthy or flawed. This emotional may manifest in self-criticism, difficulty in accepting love, or an inability to recognize personal value. Traumatic experiences can disrupt healthy attachment patterns, fostering a sense of isolation and reinforcing self-hatred. Healing requires acknowledging these wounds and reframing the narrative, allowing individuals to Separate their worth from past experiences. Professional guidance and self-compassion are essential in navigating this complex process, helping to transform shame into self-understanding and empowerment. By addressing these root causes, individuals can begin to rebuild their sense of self and foster a more compassionate relationship with themselves.
Societal and Cultural Influences
Societal and cultural expectations play a significant role in shaping feelings of shame and self-hatred. Many individuals internalize messages from their environment, such as unrealistic beauty standards, gender roles, or perfectionism, leading to self-criticism when these ideals are not met. Cultural norms often emphasize achievements and external validation, fostering a sense of inadequacy when personal goals are unfulfilled. Additionally, societal stigma surrounding mental health, sexuality, or body image can deepen feelings of shame. Recognizing these external influences is crucial to understanding their impact on self-perception. By challenging these societal narratives and embracing individuality, individuals can reduce the grip of shame and cultivate a more compassionate self-view. Addressing these cultural factors is an important step in the journey toward healing and self-acceptance.
Personal Experiences and Negative Self-Talk
Personal experiences, particularly those involving criticism or rejection, can significantly contribute to shame and self-hatred. Negative self-talk, often rooted in past traumas or unresolved emotions, exacerbates these feelings by reinforcing self-doubt and inadequacy. When individuals repeatedly engage in self-criticism, it can become a deeply ingrained habit, making it difficult to recognize their worth. This cycle of self-deprecation can hinder personal growth and lead to mental health challenges. Addressing negative self-talk involves acknowledging its origins and actively reframing harmful thoughts into compassionate ones. By practicing self-kindness and challenging unhelpful narratives, individuals can begin to dismantle the foundation of self-hatred and work toward a more balanced and positive self-image. Breaking this cycle is essential for healing and fostering a healthier relationship with oneself;

Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms

Recognizing signs of shame and self-hatred involves identifying emotional and behavioral indicators, such as self-criticism, withdrawal, and self-sabotage, which can manifest both internally and externally, affecting daily life.

Emotional and Behavioral Indicators
Emotional indicators of shame and self-hatred often include intense self-criticism, feelings of worthlessness, and persistent guilt. Individuals may struggle with low self-esteem, difficulty accepting praise, or a tendency to overgeneralize negative experiences. Behaviorally, this can manifest as social withdrawal, self-sabotage, or perfectionism. Some people may exhibit passive or defensive behaviors, while others might struggle with self-care or engage in harmful coping mechanisms. These emotional and behavioral patterns often stem from unresolved trauma, negative self-talk, or internalized societal expectations. Recognizing these signs is crucial for addressing the root causes of shame and self-hatred. By acknowledging these indicators, individuals can begin to break free from destructive thought cycles and work toward healing and self-compassion.
Physical Manifestations of Shame
Shame can manifest physically, often as tension, numbness, or discomfort in the body. Common signs include slouched posture, avoiding eye contact, or a sinking feeling in the chest. Some individuals may experience physical pain, such as headaches or gastrointestinal issues, as shame triggers the body’s stress response. Chronic shame can lead to long-term health problems, like weakened immunity or cardiovascular issues, due to prolonged emotional distress. Additionally, self-hatred may express itself through self-destructive behaviors, such as substance abuse or neglecting physical needs. These physical symptoms often mirror the emotional turmoil, highlighting the deep connection between mental and physical health. Recognizing these manifestations is essential for addressing the root causes of shame and beginning the healing process.

Strategies for Overcoming Shame and Self-Hatred
Effective strategies include mindfulness, self-compassion, and reframing negative thoughts. Practices like journaling, meditation, and positive affirmations help build self-worth and foster emotional resilience.
Mindfulness and Self-Compassion Practices
Mindfulness and self-compassion are powerful tools to address shame and self-hatred. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can observe their emotions without judgment, fostering a sense of acceptance. Self-compassion encourages treating oneself with kindness, especially during difficult times. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and grounding exercises help calm the mind and reduce self-criticism. Journaling about emotions and engaging in acts of self-care can also promote healing. These practices help shift focus from self-judgment to understanding and compassion, creating a foundation for emotional resilience and personal growth. Regularly incorporating these strategies can lead to lasting changes in how one perceives and interacts with themselves, fostering a more positive and supportive inner dialogue.
Challenging and Reframing Negative Thoughts
Challenging and reframing negative thoughts is a crucial step in overcoming shame and self-hatred. Often, these emotions stem from deeply ingrained, harmful beliefs about oneself. By identifying and questioning the validity of these thoughts, individuals can begin to dismantle their oppressive grip. Cognitive-behavioral techniques, such as thought restructuring, encourage replacing self-critical narratives with balanced, compassionate ones. For example, instead of thinking, “I am worthless,” one might reframe it as, “I made a mistake, but I can learn from it.” This process fosters self-awareness and reduces the intensity of negative emotions. Over time, practicing this skill helps build resilience and promotes a more constructive, empowering inner dialogue. It’s a gradual process, but one that can lead to profound shifts in self-perception and emotional well-being.
Building Self-Worth Through Positive Affirmations
Building self-worth through positive affirmations is a powerful tool for countering shame and self-hatred. Affirmations are intentional, positive statements that help rewire negative thought patterns and foster self-compassion. By consistently practicing affirmations, individuals can gradually shift their self-perception from one of criticism to one of acceptance and value. For example, repeating phrases like “I am deserving of love and respect” or “I am capable and strong” can help diminish feelings of inadequacy. It’s important to choose affirmations that resonate personally and to recite them with conviction, even when they feel uncomfortable at first. Over time, this practice can strengthen self-confidence, encourage self-forgiveness, and create a more nurturing relationship with oneself. Consistency is key, as lasting change emerges from repeated, heartfelt effort.


Seeking Support and Professional Help
Professional therapy is crucial for addressing deep-seated shame and self-hatred, offering a safe space to explore emotions and develop coping strategies with guidance from trained specialists.
The Role of Therapy in Healing
Therapy plays a vital role in healing from shame and self-hatred by providing a safe and non-judgmental environment to explore and understand the roots of these emotions. Trained therapists help individuals identify negative thought patterns and behaviors that perpetuate self-hatred, offering tools to reframe these perspectives. Through techniques like cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness, and compassion-focused exercises, therapy empowers individuals to develop a more positive self-image. It also addresses underlying issues such as childhood trauma or societal influences, fostering emotional resilience and self-acceptance. By guiding individuals through the process of acknowledging and processing their emotions, therapy facilitates long-term healing and personal growth, enabling individuals to move beyond shame and self-hatred toward a more fulfilling life.
Support Groups and Community Sharing
Support groups and community sharing provide a powerful platform for individuals to overcome shame and self-hatred by connecting with others who share similar experiences. These groups foster a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation, allowing members to openly discuss their struggles without fear of judgment. Sharing personal stories and hearing others’ journeys can validate emotions and offer new perspectives, helping individuals recognize they are not alone. The collective support and encouragement within these communities can build resilience and promote healing. Additionally, group activities often include practical strategies and coping techniques, further empowering individuals to manage their emotions and work toward self-compassion and acceptance. This collective approach not only aids in personal growth but also strengthens the ability to live a more authentic and fulfilling life free from the burden of shame and self-hatred.

Maintaining Mental Health and Well-Being
Prioritizing self-care, setting healthy boundaries, and cultivating gratitude are essential for mental well-being. Engaging in activities that bring joy and practicing mindfulness can foster emotional balance and resilience.
Practicing Self-Care and Boundaries
Practicing self-care is a cornerstone of healing from shame and self-hatred. Engaging in activities that bring joy and comfort helps rebuild self-worth. Setting healthy boundaries is equally important, as it protects emotional energy and fosters a sense of control. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing, can create space for self-compassion and reduce self-criticism. Prioritizing rest and physical well-being, like exercise and a balanced diet, supports mental health. Learning to say “no” without guilt and surrounding oneself with supportive people are vital steps in maintaining boundaries. By consistently nurturing both body and mind, individuals can gradually shift from self-hatred to self-acceptance, creating a foundation for long-term well-being.
Cultivating Gratitude and Joy
Cultivating gratitude and joy is a powerful way to counteract shame and self-hatred. By focusing on what brings happiness, individuals can shift their mindset from negativity to positivity. Gratitude practices, such as journaling or daily reflections, help acknowledge life’s small pleasures, fostering a sense of abundance. Engaging in joyful activities, like hobbies or spending time in nature, uplifts the spirit and distracts from self-critical thoughts. Mindfulness exercises can enhance the ability to appreciate the present moment, reducing the grip of shame. Surrounding oneself with positive influences and celebrating personal achievements further nurtures joy. Over time, these practices can help replace self-hatred with self-appreciation, fostering resilience and emotional well-being. Consistently prioritizing gratitude and joy creates a foundation for healing and a more compassionate relationship with oneself.






























